The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is an integral component of modern electronics, facilitating the connection and function of electronic components. From humble beginnings to cutting-edge innovations, the journey of PCB technology is a testament to engineering prowess and technological advancement. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the historical development of PCB technology, highlight key innovations, and examine how these advancements have shaped the industry.
The Origins of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Technology
Early Beginnings
The concept of a PCB can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for more reliable and compact electronic connections became apparent. The first PCBs were rudimentary, involving a simple process of etching conductive paths onto a flat surface.
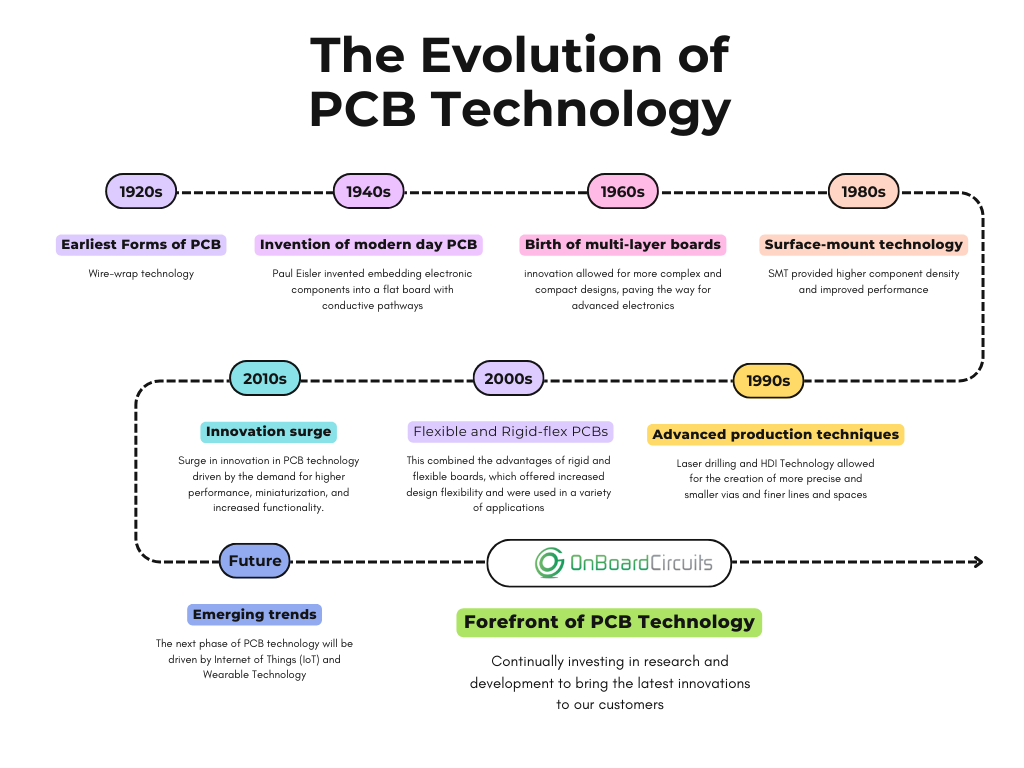
- 1920s-1930s: The earliest forms of PCBs were created using a technique called “wire-wrap” technology, where wires were wrapped around pins on a board. However, this method was cumbersome and limited in scalability.
The Advent of Modern PCB Technology
- 1940s: The invention of the PCB as we know it today is credited to Paul Eisler, an Austrian engineer. Eisler’s design involved embedding electronic components into a flat board with conductive pathways. This innovation was initially used in military applications during World War II.
- 1950s: The use of PCBs expanded to consumer electronics, including radios and televisions. This period saw the introduction of printed circuit boards in various shapes and sizes, significantly improving the reliability and durability of electronic devices.
Key Innovations in PCB Technology
The 1960s: The Birth of Multilayer PCBs
The 1960s marked a significant milestone with the introduction of multilayer PCBs. Unlike single-layer PCBs, multilayer boards consist of multiple layers of conductive material separated by insulating layers. This innovation allowed for more complex and compact designs, paving the way for advanced electronics.
- Innovation: Multilayer PCBs enabled the integration of more components and functions into a single board, leading to the development of more sophisticated electronic devices.
The 1980s: Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)
The 1980s brought about the adoption of Surface-Mount Technology (SMT), a method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of the PCB. SMT offered several advantages over traditional through-hole mounting, including:
- Higher Component Density: SMT allows for a higher density of components on the PCB, leading to more compact and lightweight designs.
- Improved Performance: SMT reduces the length of electrical connections, resulting in better signal integrity and performance.
The 1990s: Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
The 1990s saw the introduction of advanced manufacturing techniques, including:
- Laser Drilling: Laser drilling technology allowed for the creation of more precise and smaller vias (holes) in PCBs, improving the overall quality and reliability of the boards.
- High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Technology: HDI PCBs featured finer lines and spaces, allowing for higher component densities and improved performance in high-speed applications.
The 2000s: Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs
The early 2000s witnessed the rise of flexible and rigid-flex PCBs, which combined the advantages of rigid and flexible boards. These PCBs offered increased design flexibility and were used in a variety of applications, including:
- Consumer Electronics: Flexible PCBs found applications in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.
- Automotive Industry: Rigid-flex PCBs were used in automotive electronics, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Modern Innovations in PCB Technology
The 2010s and Beyond: Advanced Materials and Techniques
The last decade has seen a surge in innovation in PCB technology, driven by the demand for higher performance, miniaturization, and increased functionality.
- High-Frequency PCBs: With the growth of 5G and other high-frequency applications, PCBs made from advanced materials like Teflon and ceramics have become essential for managing high-speed signals and minimizing signal loss.
- Printed Electronics: Advances in printed electronics have enabled the creation of PCBs using conductive inks and printing techniques, allowing for even more flexible and innovative designs.
The Future of PCB Technology
As we look to the future, several emerging trends are poised to shape the next phase of PCB technology:
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices is driving the demand for smaller, more integrated PCBs with advanced connectivity features.
- Wearable Technology: Innovations in wearable technology require PCBs that are not only compact but also flexible and durable.
How OnBoard Circuits Is Leading the Way
At OnBoard Circuits, we are at the forefront of PCB technology, continually investing in research and development to bring the latest innovations to our customers. Whether you’re looking for advanced multilayer PCBs, flexible circuits, or high-frequency solutions, we have the expertise and technology to meet your needs. Check out our product capabilities.
PCB technology has been marked by continuous innovation and improvement, from its early beginnings to the sophisticated designs of today. As we move forward, the demand for more advanced, reliable, and compact PCBs will continue to drive the industry. At OnBoard Circuits, we are committed to staying ahead of the curve and providing our customers with cutting-edge solutions that meet the ever-evolving demands of the electronics industry.
Stay updated with the latest in PCB technology and industry trends by subscribing to our newsletter. For customized PCB solutions or to request a quote, contact our team today. Let OnBoard Circuits be your partner in innovation!